Climate Change
Basic Policy on Environment
We will actively address environmental issues and aim to balance between a rich environment in the future and business activities.
Responding to Climate Change
Keihanshin Building recognizes that the climate change problem brings about dramatic changes to the natural environment and social structure, and that it is a key issue (materiality) that has an impact on our Company's overall management and business. Based on this recognition, we evaluate the impact of long-term and highly uncertain climate change on our business, and respond appropriately to medium- to long-term changes including the transition toward a decarbonized society and physical impacts such as climate change and rising sea levels, by building the corporate structure, enhancing the efficiency of energy use, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and other means.
Policy for Resilience to Climate Change [PDF:289KB]
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Reduction Policy [PDF:93KB]
Energy Conservation Policy [PDF:87KB]
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations
In November 2021, the Company announced its endorsement of the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures (TCFD). Taking this opportunity, the Company is assessing the impact of climate change on its business, and from June 2022, has been disclosing climate change-related information in line with the framework recommended by the TCFD.
In view of the need to enhance information disclosure on the financial impact that climate change and other sustainability issues have on a company, which enables investors to make appropriate investment decisions, the Company recognizes anew that initiatives to address climate change and other sustainability issues will contribute to the medium- to long-term enhancement of its corporate value.
Information Disclosure Based on TCFD Recommendations [PDF : 2,414KB]

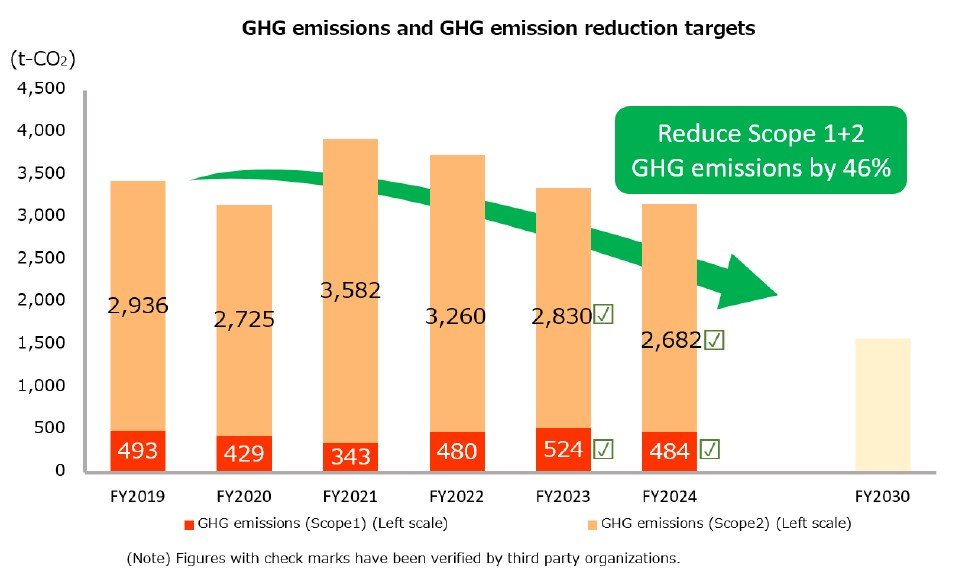
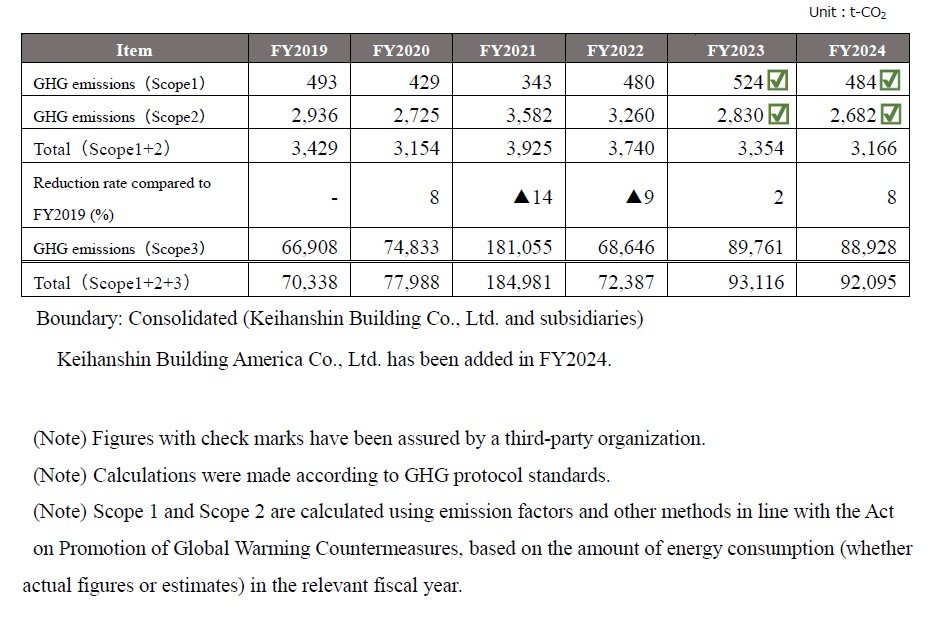
The GHG emissions in fiscal 2024 (Scope1 and Scope2) have been verified by a third-party organization.
Assurance Report[PDF : 60KB]
Indicators and Targets
GHG emissions
KPI: |
Reduce GHG emissions (Scope 1 and 2) by 46% by FYE March 2031 (compared to the FYE March 2020)
|
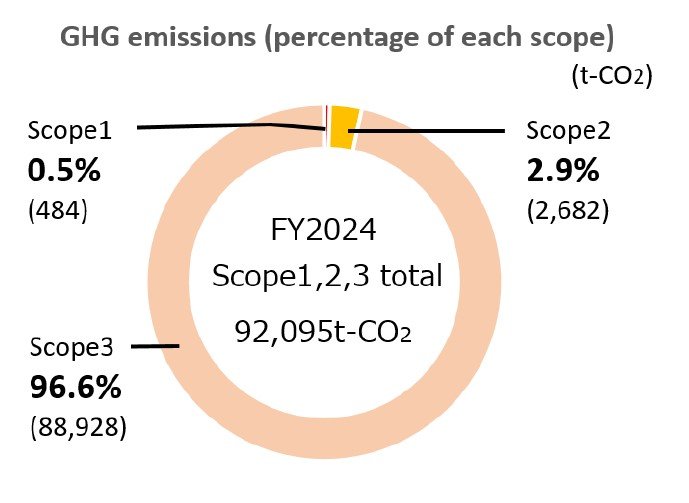
In the fiscal year ended March 31, 2025, Scope 3 GHG emissions accounted for about 97% of the Company's total supply chain GHG emissions. Of Scope 3 GHG emissions, approximately 88% are GHG emitted by the business activities of tenants (customers) of our leasing properties (Category 13), and approximately 85% of the Company's total supply chain GHG emissions consists of those emitted by the business activities of tenants (customers) of our leasing properties. This distinctive figure is due to the fact that we lease datacenter buildings.
Compared to office buildings, datacenter buildings use a larger amount of electricity to operate and cool IT equipment. However, we believe that we are making a certain contribution to energy conservation and GHG emissions reduction in society as a whole through efforts such as having datacenter users transfer and consolidate their servers and other IT equipment scattered across multiple locations into a state-of-the-art datacenter building with high energy efficiency.
We believe that in order to reduce GHG emissions across the entire Company, it is essential to promote energy conservation initiatives in cooperation with tenants (customers) and encourage them to consider the use of renewable energy. We will continue to work to reduce GHG emissions in cooperation with tenants (customers).
Use of renewable energy
KPI: |
100% of the electricity used by the Company under Scope 2 shall come from
|
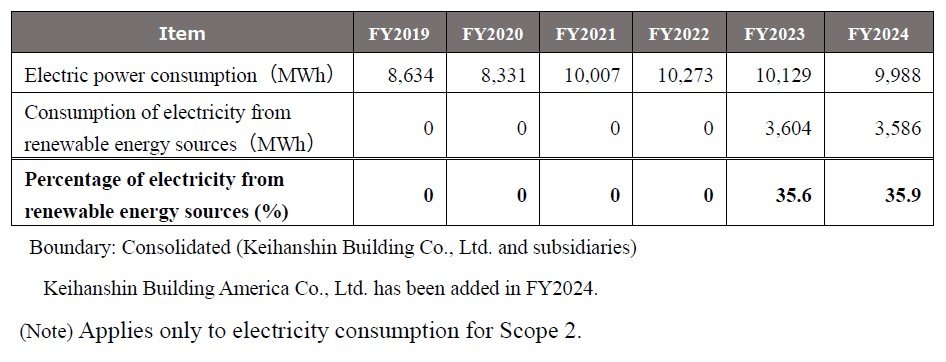
To reduce GHG emissions associated with energy consumption, in addition to promoting energy-saving measures, the Company is also working to introduce power from renewable energy sources. Since the fiscal year ended March 2024, multi-tenanted office buildings and some of the Company's properties have switched to using electricity from renewable energy sources. In addition to purchasing electricity from external suppliers, solar panels are installed on the rooftop of Keihanshin Fuchu Building.
 Solar panels on the Keihanshin Fuchu Building
Solar panels on the Keihanshin Fuchu Building
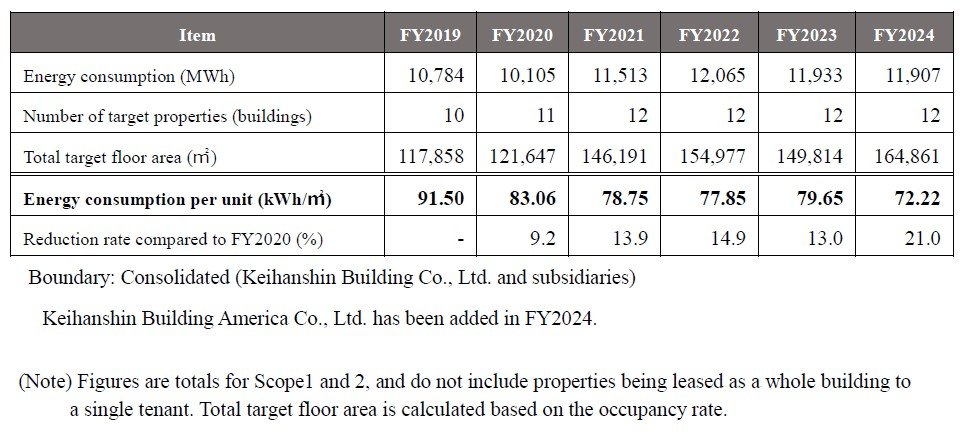
Acquisition of Green Building Certification
Acquisition of Green Building Certification
KPI: |
Raise the ratio of the area of properties with the Green Building Certification to
|
We promote the acquisition of green building certifications, such as CASBEE Real Estate Certification and BELS Certification, in order to objectively assess the condition of our buildings through external evaluations, and at the same time, to use them as a reference for further improvement and enhancement.
Overview of CASBEE Real Estate Certification
The CASBEE (Comprehensive Assessment System for Building Environmental Efficiency) is a method for rating the environmental performance of buildings. The method comprehensively assesses building quality, including interior comfort and attention to the surrounding scenery, in addition to care for the environment (such as use of materials and equipment that conserve energy with a minimal environmental impact). For more information on CASBEE, please see the link below.
CASBEE Real Estate Certification assessment ranking
The CASBEE Real Estate Certifications we have obtained are as follows:

CASBEE Real Estate Certification (in order of acquisition)
| Midosuji Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Fuchu Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Yodoyabashi Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Toranomon Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Onarimon Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Yoyogi-koen Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Fujisawa Shopping Facility | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| WINS Umeda B Building | Rank S ★★★★★ |
| Kawaramachi Building | Rank A ★★★★ |
| Komaki Logistics Center | Rank B+ ★★★ |
Overview of BELS Certification
BELS (Building-Housing Energy-efficiency Labeling System) assesses and labels non-residential buildings in terms of energy conservation performance, etc. based on the Evaluation Guidelines for Indicating Energy Conservation Performance of Non-Housing Buildings (2013) established by Japan's Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism (MLIT). BELS uses an assessment method that conforms to the revised Energy Conservation Standards (fully enforced on April 1, 2014). For more information on BELS, please see the link below (available in Japanese only).
BELS Certification assessment ranking
The BELS Certification we have obtained is as follows:
BELS Rating
| OBP Building | Two Stars ★★ |
Of net sales of 19.3 billion yen for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2024, net sales from nine properties with green building certifications are 7.0 billion yen, accounting for approximately 36% of total net sales.
High energy conservation performance (example of the Toranomon Building)
The Toranomon Building uses airflow windows*, a zoned air conditioning system, and LED lighting for system ceilings. The building contributes to reducing the burden on the environment with its high-spec energy-conservation performance, such as automatic light adjustment by sensors. * Airflow is directed between an outer and an inner layer of glass, mitigating the afternoon sun in summer and the cold in winter, and achieving both comfort and energy conservation.
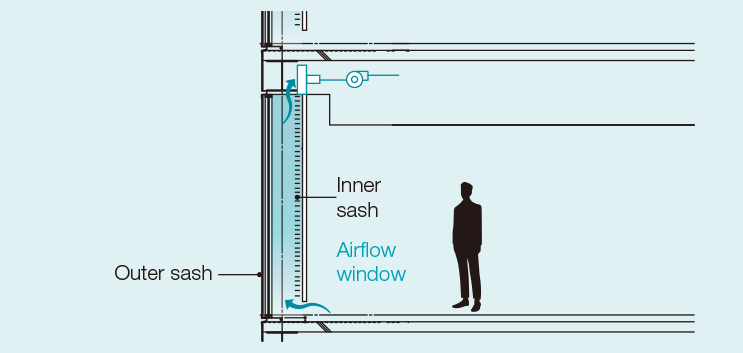 Cross-section view of an airflow window
Cross-section view of an airflow window

